Two Terminal Semiconductor Devices
Two Terminal Devices
1. There are many two terminal devices which has a single P-N junction such as zener diode, varactor diode, schottky diode, tunnel diode etc. Let’s discuss them all.
2. Zener Diode :
a. Zener diode also known as the breakdown diode is designed to work in the breakdown region in the reverse bias condition.
b. It should be properly doped . this means that the characteristics of the zener are all related to its doping. If it is heavily doped then thin depletion layer and low zener voltage.
c. Silicon is preferref for zener diode over germanium because of higher operating point and current capability.
d. Works in reverse bias.
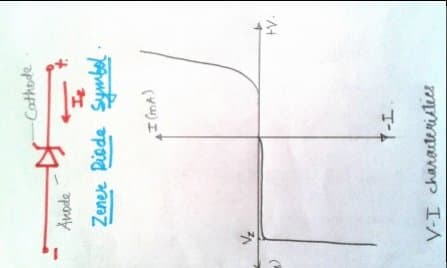
e. Applications of zener diode:
i. Zener is used for voltage regulation(later discuss in detail)
ii. Meter protection
iii. Zener as a reference element.
3. Tunnel diode:
a. It’s a high conductivity P-N junction device which is heavily doped about 1000 times that of the conventional diode.
b. Depletion region is very small of the order of 10^-5mm because of which the carriers move through with the speed of light even if they do not have the energy to overcome its potential barrier.
c. Thus a large forward current is produced.
d. Such a mechanism where the charge carriers punch through the barrier directly is called as tunneling.(a route or a tunnel is produced for the flow of carriers). Thus called tunnel diode
e. Only works in forward bias. Also called as Esaki diode
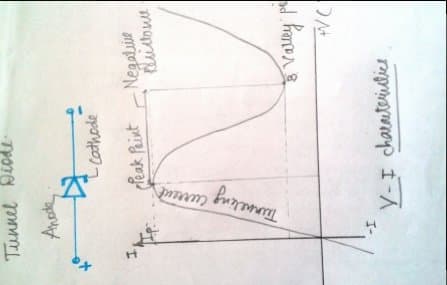
f. Applications: It can be used as an amplifier, oscillator or switch.
4. Varactor diode:
a. Varactor diode is a semiconductor, voltage dependent, variable capacitor. Also called as varicap, VVC, voltcap etc.
b. Its works in reverse bias, i.e its mode of operation is based on transition capacitance.
c. The working is based on the same principle of transition capacitance. The depletion region serves as the dielectric.
d. Application: It is used as a tuning circuit.
Updated Answer:
This is an old discussion and I thought I’d present the answer in the form of a detailed article so that it’s easier to understand semiconductor devices with two terminals.
Two Terminal Semiconductor Devices: A Detailed Examination
Introduction
Two-terminal semiconductor devices are the foundation stones of modern electronics, shaping the technological advancements we see today.
Despite their seeming simplicity, these devices fulfil a fundamental role in electronic circuits.
This article will delve into various two-terminal semiconductor devices, particularly diodes such as the standard p-n diode, Zener diode, varactor diode, Schottky diode, and tunnel diode.
Basics of Semiconductor Devices
Understanding two-terminal semiconductor devices begins with comprehending the very essence of semiconductors.
They possess intermediate electrical conductivity, sitting between conductors like copper and insulators like rubber. Semiconductors' distinct conductivity is attributable to their unique atomic structure and electron arrangement.
Semiconductor conductivity can be dramatically altered by a process known as 'doping', which involves intentionally infusing impurities into a highly pure semiconductor to increase the number of charge carriers (free electrons in n-type semiconductors and holes in p-type semiconductors).
The junction of p-type and n-type semiconductors forms the cornerstone of most semiconductor devices.
Overview of Two Terminal Semiconductor Devices
P-N Diodes
P-N diodes, the most fundamental two-terminal semiconductor devices, comprise a single p-n junction that permits current flow solely from the anode (p-side) to the cathode (n-side).
This rectification property is pivotal in the conversion of alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC).
Zener Diodes
Zener diodes are distinctive in their ability to conduct in the reverse direction when the voltage surpasses a certain threshold, known as the Zener voltage.
Their unique characteristic makes them ideal for voltage regulation and surge suppression, serving as an electronic component that clamps the voltage to a predefined maximum level.
Schottky Diodes
Schottky diodes, named after the German physicist Walter H. Schottky, possess a low forward voltage drop and swift switching action.
This makes them particularly suitable for applications requiring high efficiency and fast response times, such as in power rectifiers and radio frequency (RF) applications.
Varactor Diodes
Varactor diodes, also known as varicap diodes or tuning diodes, have a p-n junction with a variable capacitance that depends on the applied reverse bias voltage. As the bias voltage varies, so does the diode's capacitance. This feature makes varactor diodes essential for frequency modulation and tuning applications, such as in television sets and radio receivers.
Tunnel Diodes
Tunnel diodes are noted for their negative resistance, meaning they can actually amplify signals, a rare property in two-terminal devices. These diodes leverage a quantum mechanical effect called tunneling, leading to fast operation. They were historically used for microwave and high-speed switching applications, though they have been largely superseded by newer technologies.
Conclusion
Two-terminal semiconductor devices are ingrained in numerous applications. From p-n diodes critical for AC to DC conversion, Zener diodes for voltage regulation, Schottky diodes for high-efficiency applications, to varactor diodes for frequency modulation, these simple yet versatile devices play a pivotal role in shaping the electronic landscape.
Their continued evolution fuels technological innovation, underscoring their importance in our modern, interconnected world.
Let me know if this article is helpful. If you have follow-up questions about any of the above mentioned diodes, ask in the comments below.
Replies
-
 a.alandkarHello Prajakta, Its really nice that you are sharing basic electronics concepts. But if possible add some more explaination like (in this blog you may add how z-diode works i.e. the concept of zener breakdown), which would be really helpful to the beginners.
a.alandkarHello Prajakta, Its really nice that you are sharing basic electronics concepts. But if possible add some more explaination like (in this blog you may add how z-diode works i.e. the concept of zener breakdown), which would be really helpful to the beginners. -
 Santhosh MInformative...👍
Santhosh MInformative...👍 -
 Prajakta Kelapure
Prajakta Kelapure
hello,a.alandkarHello Prajakta, Its really nice that you are sharing basic electronics concepts. But if possible add some more explaination like (in this blog you may add how z-diode works i.e. the concept of zener breakdown), which would be really helpful to the beginners.
Yes i am trying to include as much as stuff I can. I appreciate you for letting me know a few more topics.
You are reading an archived discussion.
