What is directory in Linux & What Is Parent Directory In Linux?
Also what are pathnames in linux. I really can't get these things in my head.😨
please help
Member • Aug 6, 2013
Yes directories are analogous to folders in windows. Parent directory is the directory in which the child directory resides. Suppose the directory path is /home/support/xyz then support is the parent directory of xyz.pradeep.pawarWhat is a directory in linux and what is parent directory? Are they folders or files?
Also what are pathnames in linux. I really can't get these things in my head.😨
please help
Member • Aug 6, 2013
Thanks Nick for such a explanation.Nick_SharmaYes directories are analogous to folders in windows. Parent directory is the directory in which the child directory resides. Suppose the directory path is /home/support/xyz then support is the parent directory of xyz.
Path names are the paths that lead to a particular directory. there are 2 types of paths
-> absolute path: complete path from root to the directory
-> relative path: path from current directory to another directory
Let me know if you still have doubts
Member • Aug 6, 2013
Directory is a folder as in Windows matepradeep.pawarThanks Nick for such a explanation.
But then can directory be considered as a folder like in windows
Member • Aug 6, 2013
ThanksConquerorDirectory is a folder as in Windows mate
Root Directory is like My Computer From which all folders can be easily opened
PS: Just an example
Member • Aug 6, 2013
what folder are they in?pradeep.pawarThanks
#-Link-Snipped-#
Member • Aug 6, 2013
Root includes every directory : /boot,/lib,/mnt,/dev etc etc.pradeep.pawarThanks
Conqueror, then all software and programs we get from software centre installed , are they in root itself
Member • Aug 6, 2013
ThanksAbhishek RawalRoot includes every directory : /boot,/lib,/mnt,/dev etc etc.
Don't mix up '/root' with '/' : /root is SU home directory, while / is root of entire File system.
But applications are usually stored in :
/usr/bin
/bin
/sbin
/usr/sbin
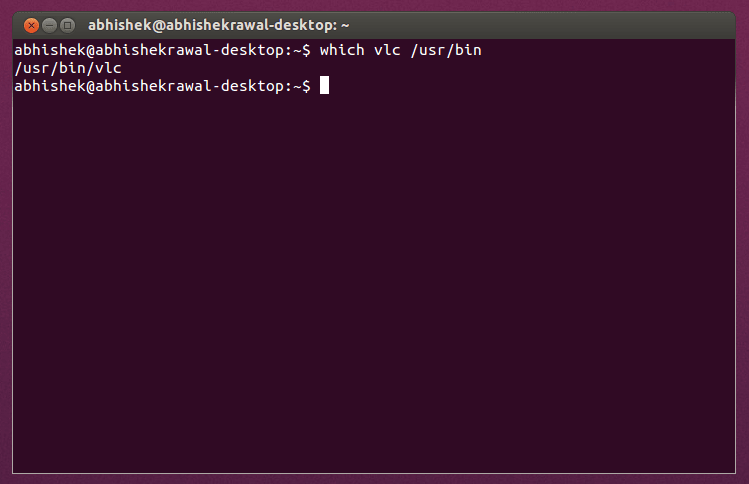
You can locate the desired binaries using 'which' or can locate all installed binaries in /usr/bin using 'ls'.
example :
For more information on Linux File-system : Read #-Link-Snipped-#
PS : There might be grammatical mistake & book is still not completed. But whatever information it contains, is correct.