Scientists Uncover The Internal Structure Of Kerogen
Scientists and engineers from MIT along with the French government’s research organization, CNRS have discovered the actual structure of Kerogen, the solid hydrocarbon which is the main constituent of contemporary non-renewable fuels. Kerogen is a mixture of organic chemical compounds, a material that makes up sedimentary rocks. Refinement of such underground deposits, gives us potential fuels such as Petroleum, Natural Gas etc. After a long and difficult journey, researchers were finally able to get a breakthrough on its structure.
Kerogen, as mentioned earlier, is recovered from buried plants, microbes and animals that have decomposed and got compressed over several years. This porous carbon-rich, rock-hard material melts into a fluid state under extreme geo thermal pressure and heat and flows through the porous structure. The latest study reveals that hydrocarbon fluids do not follow the Darcy equation when it is underground, inside the Kerogen structure.
Pellenq, a senior research scientist in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering at MIT explained that the flux in nanoscaled pores showed a different behaviour when compared to fluid movements in a macroscale structure. The nanosized openings often block the flow and stores the fluid like a water barrage.
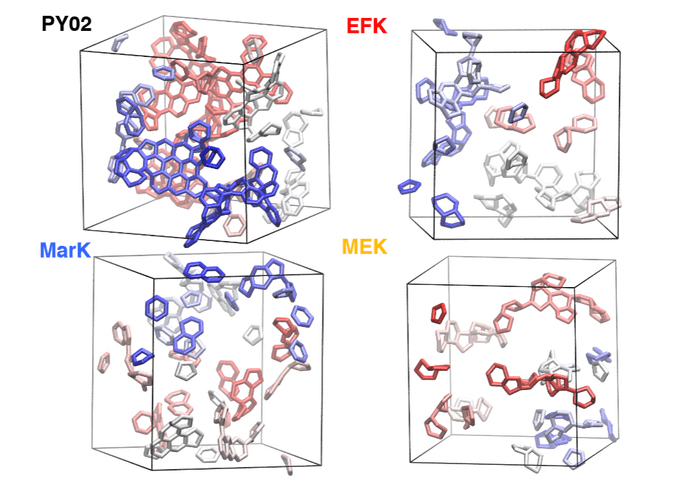
Visualization of the aromatic clusters in the kerogen samples
According to Pellenq, their research would benefit the refinery industries where fluids are extracted from small channels. With the help of the new findings, the fracking process would touch the real treasure that is present behind the porous gates. Being hydrophobic, the structural pores retard the hydrofracking process. However, if the water based fluids are replaced with carbon-dioxide based fluid fracking, the pores would allow them to pass through being CO2-philic. This method might also effectively stop the water based contamination in the process.
Jean-Noël Rouzaud, the CNRS research director at the geology laboratory of the Ecole Normale Supérieure in Paris claimed that the initiation of such a methodology was a pioneering move by the team and that in the future more such effective and environment-friendly techniques could be used to recover the hydrocarbons. Their results were published in the journal Nature Materials, titled “Realistic molecular model of kerogen’s nanostructureâ€.
Source: <a href="https://news.mit.edu/2016/structure-kerogen-revealed-0201" target="_blank" rel="nofollow noopener noreferrer">Structure of kerogen revealed | MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology</a> | #-Link-Snipped-#
Kerogen, as mentioned earlier, is recovered from buried plants, microbes and animals that have decomposed and got compressed over several years. This porous carbon-rich, rock-hard material melts into a fluid state under extreme geo thermal pressure and heat and flows through the porous structure. The latest study reveals that hydrocarbon fluids do not follow the Darcy equation when it is underground, inside the Kerogen structure.
Pellenq, a senior research scientist in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering at MIT explained that the flux in nanoscaled pores showed a different behaviour when compared to fluid movements in a macroscale structure. The nanosized openings often block the flow and stores the fluid like a water barrage.

Visualization of the aromatic clusters in the kerogen samples
According to Pellenq, their research would benefit the refinery industries where fluids are extracted from small channels. With the help of the new findings, the fracking process would touch the real treasure that is present behind the porous gates. Being hydrophobic, the structural pores retard the hydrofracking process. However, if the water based fluids are replaced with carbon-dioxide based fluid fracking, the pores would allow them to pass through being CO2-philic. This method might also effectively stop the water based contamination in the process.
Jean-Noël Rouzaud, the CNRS research director at the geology laboratory of the Ecole Normale Supérieure in Paris claimed that the initiation of such a methodology was a pioneering move by the team and that in the future more such effective and environment-friendly techniques could be used to recover the hydrocarbons. Their results were published in the journal Nature Materials, titled “Realistic molecular model of kerogen’s nanostructureâ€.
Source: <a href="https://news.mit.edu/2016/structure-kerogen-revealed-0201" target="_blank" rel="nofollow noopener noreferrer">Structure of kerogen revealed | MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology</a> | #-Link-Snipped-#
0
