Software (Manual) Testing Interview questions
1. Tell us about yourself? (This is to know the person and assess the communication skills)
Answer: This is a very personal question. You should briefly introduce yourself with details about your education, work experience and maybe career goals.
2. What is testing life cycle?
Answer: In general, software testing life cycle is a collection of various steps executed to ensure that the final product can be of the acceptable quality. The general steps in STLC include test planning, test analysis, test design, verification and validation and testing after implementation of the final product. It's important to note that the exact steps will vary from organisation to organisation because it's mostly defined by the policies of the organisation related to quality assurance.
3. Explain SDLC and your involvement?
Answer: SDLC is an abbreviation of software development life cycle which is basically the steps through which any software product goes through. It starts with 'requirements gathering' phase, analysis of requirements, design of the system, implementation, testing and maintenance. Though 'testing' is listed as a separate stage in the SDLC, it's important to note that testing is a continuous process that begins at the time of first phase i.e. during requirements gathering and continues until and after the system is deployed.
4. Tell us the process you follow in your organization?
Answer: This is a tricky question. You'll have to be fully aware of the various processes that are followed in your organisation to carry out the testing activities. If you're asked this question, you'll have to ask the interviewers (or tell them on your own) about the specific task for which the processes were followed in your organisation. For example, your organisation may have a process for the development of the test plan or test cases documents. You'll have to inform them the same.
5. What is boundary value analysis?
Answer: Boundary value analysis is what the name suggests - analysis at the boundary conditions. Let's say the username field in your application requires the username not to exceed 10 characters. In such a case, the boundary value analysis will be to test the field for usernames with 9 characters and 11 characters. If the test passes, then you can be reasonably sure that there is no bug.
6. Explain Equivalent Partitioning?
Answer: Though the words look like it's kind of a rocket science, in reality it's just a technique used to reduce the number of test cases. Basically, you partition the data into sets of valid and invalid inputs. I found an excellent video that explains the concept in simple language -
7. What is bug life cycle?
Answer: Bug Life Cycle, again is the various stages through which it goes after it's discovered. So once the Quality Assurance Engineer discovers the bug, it's marked as "New", then the concerned authority will assign it to the developer where the status of the bug changes to 'Assigned', once the bug is assigned it's either 'fixed' or 'rejected'. In both the cases, the QAE will verify the bug and mark it as 'reopen' (if not fixed properly) or 'closed' if it no longer exists.
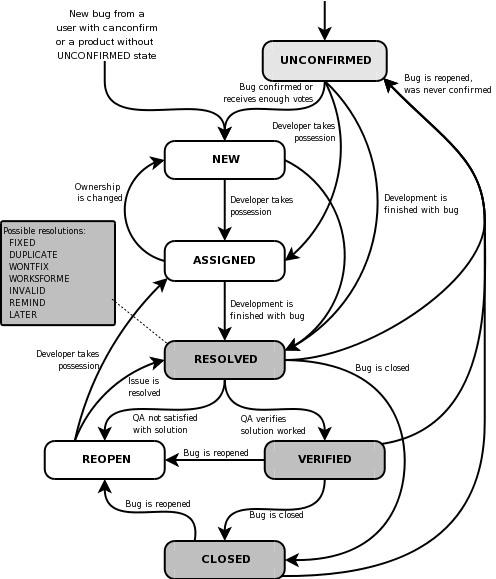
Image Source: Bugzilla.
8. How to use QC?
Answer: QC is a short of Quality Center, a software testing related tool owned by HP. If you've used this tool, you'll know how to answer.
9. What is severity and priority, explain the difference?
Answer: Severity is basically an indicator of 'how big is the impact of the discovered bug/issue' on the software and 'priority' is how urgent it is to address (fix) it. A very good example of this would be failure at the login window with valid username and password. This type of bug is not only severe but also should be fixed on high priority.
10. When do you stop testing? ( I mean when do you say, testing is done?)
Answer: Software testing never stops and in fact, should be done as a continuous process throughout the life of the software. However it's not practical. In reality, the software testing stops when the software meets the defined quality criteria.
11. What do you write in a test plan?
Answer: A test plan is a strategy document that details the various approaches, steps and procedures the software testing team will follow to ensure the product meets desired quality. A comprehensive test plan will include (but not limited to) who will test what, the resources team will use, risk strategy etc. along with a well defined scheduled. You may refer to various test plan templates available on the Internet for the details.
12. What is test strategy?
Answer: Test strategy is again a 'method' that needs to be followed to carry out testing activity. It will clearly define team member's individual roles and responsibilities, use of testing tools, deadlines to be followed, what needs to be tested, the software testing environment required and schedule that the team needs to stick to.
13. What is risk analysis?
Answer: Risk analysis is, in simpler words, the analysis of things that may go wrong and coming up with preventive measures. For example, an important team member falling sick just before the delivery would pose a bigger risk to the delivery. One possible way to mitigate this risk would be to prepare team members to handle each other's responsibilities so that the missing team member's work can be shared.
14. If you have ‘n’ requirements and you have less time how do you prioritize the requirements?
Answer: In such a scenario, the most critical requirements need to be finalised with discussion from the client. In testing, requirements aren't really 'finalised' by the testing team.
15. What all types of testing you could perform on a web based application?
Answer: A typical web based application may undergo - Functionality, Usability, Compatibility, Performance (load testing, stress testing), Security testing.
16. What is smoke testing and what is sanity?
Answer: What would happen if you turn on a newly brought TV and you get smoke coming out of it? Smoke testing is basically to ensure that the basic functionality of the product (in TV's case, it should be displaying video when turned on) works fine. So you'll identify the most basic test cases you need to execute and perform them.
Sanity testing is similar - which ensures that the system or product functions without any logical errors. If you are testing a calculator app; you may multiply a number by 9 and check whether the sum of the digits of the answer is divisible by 9.
17. How do you find the regression scenarios if a defect is fixed?
Answer: Regression scenarios would be run on all the test cases that failed during manual testing because of the bug in software. Checking history of the bug may help identifying the regression scenarios.
18. What is the difference between bug, defect and a error?
Answer: There's actually no difference between 'bug' and 'defect'. It's basically an unexpected behaviour of the software. 'Error' too would fall in the same category; but many times errors are well defined. For example - 404 error in HTML pages.
PS: Answers added by #-Link-Snipped-#.
