Osmotic Renewable Energy: A New Way To Generate Electricity
A group of scientists from Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) has recently unveiled their work that is related to clean energy and carved a new path for osmotic power alongside solar, wind and hydro power. More accurately, the potential of their research is inspired by our nature and it shows how energy could be evolved when fresh water meets sea water with the help of a membrane. The team comprising of nanoscale biology department members have created a one of a kind energy generation system with a 3 atom thick semipermeable membrane in the middle of fluids with different salt concentrations.
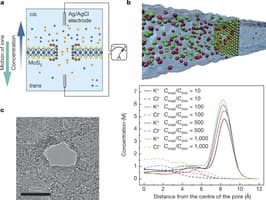
The system set-up
EPFL scientists have designed a two compartment system, in which one is filled with sea water and another with fresh water. In the middle a nano-porous membrane is stitched. While salt ions pass through the channel, the electrons are ported to an electrode, the key element to devise electricity. Owing to the membrane’s property, the positive ions are pushed through whereas negative ions were driven away, this action maintains a certain voltage in two different compartments which ultimately generates electricity.

The team revealed that the pore structure was very important for them to decide as larger or smaller than the accurate size would have complicated the process and might cease the system from running. The membrane is made of molybdenum disulfide and depending on its thinner structure, electricity increases.
Application wise, it produces a huge impact with 1MW of electricity if passed through 1 m^2 membrane featuring 30% of its surface covered with pores. Plus the membrane is easy to reproduce with chemical vapor deposition. The greater challenge is to scale up the performance which could be realized, incorporating uniform pores. According to the team, if the system could be further developed then it will soon be a potential form of renewable energy. The complete research was published in Nature.
Source: #-Link-Snipped-#
