New Super Multi-View Technique Forms 3D Image Without Straining The Eye
A team of researchers from the Sun Yat-Sen University in China has taken a novel approach towards incorporating 3D image viewing in portable smart electronic devices by minimising a viewer’s discomfort. Including three dimensional visual effects requires more effort for manufacturing. Moreover, the expected slim design and stylish body features in a smartphone gives a hard time to 3D enabled screens.
Owing to the “super multi-view techniqueâ€, the team significantly decreased the number of micro-displays required, which in turn also helped in a compact system design. Lilin Liu, author and an associate professor at the State Key Lab of Optoelectronics Materials and Technology at Sun Yat-Sen University in China, explained that human eyes experience stress due an ophthalmic phenomenon known as vergence-accommodation. Due to a 6-inch gap between the eyes, when concentrating on a single image, the image appears slightly different to each eye.
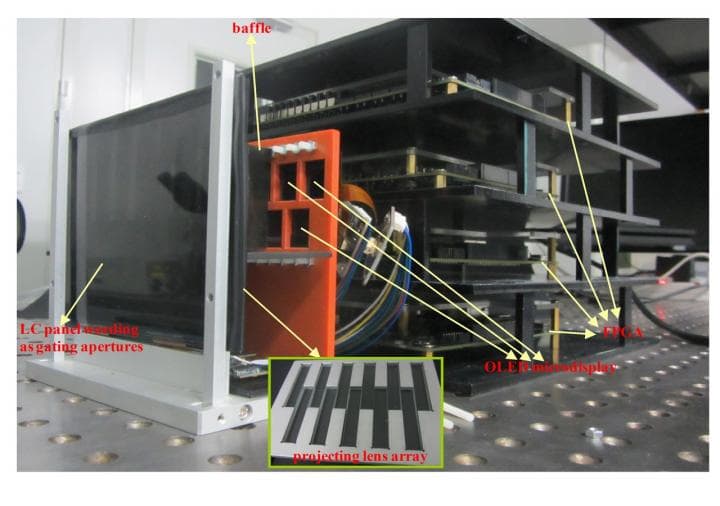
A super multi-view (SMV) system with comfortable 3-D effects
To maintain the binocular vision, the brain directs the eyes to maintain the focus of the lens within each eye so that the image projects sharply on the retina. The distance at which the eyes' sight lines cross is known as vergence distance whereas the distance to which the eye is focused is known as the accommodative distance. Vergence-accommodation emerges when the focal point and convergence point of eyes on an image fail to work in sync with each other.
Naturally, the human eye vergence and accommodation synchronize with each other which ensures the appearance of an undistorted image in front of the eyes. An Artificial 3D pictures manipulates the vergence-accommodation relation by imitating the natural viewing process. Though they tend to change the vergence distance in a 3D landscape, the eye accommodation distance remains constant, raising eye irritation and discomfort.
Liu explained that the current 3D systems give an output of some views of the displayed spatial spot to a single eye pupil. Due to such an operation, the accommodation distance neglects the key phenomenon in order to adjust with the vergence distance. The team came up with a solution, in which they would provide two viewpoints to the pupil. The team designed a prototype having 11 elementary projecting units, each of which boasts of organic light-emitting diode (OLED) micro display, a rectangular projecting lens, two vertical baffles and a pile of gating apertures (liquid crystal panel) attached to the projecting lens. Adjusting the gating apertures with a corresponding micro display results in dense viewpoints on the display screen.
Liu asserted that the main strength of their project is its applicability in thin structures and its prospective vast scope to emerge as a replacement to modern screen technology in smart wearables. The detailed report of this project was published in the journal Optics Express, from The Optical Society (OSA).
Source: #-Link-Snipped-#
Owing to the “super multi-view techniqueâ€, the team significantly decreased the number of micro-displays required, which in turn also helped in a compact system design. Lilin Liu, author and an associate professor at the State Key Lab of Optoelectronics Materials and Technology at Sun Yat-Sen University in China, explained that human eyes experience stress due an ophthalmic phenomenon known as vergence-accommodation. Due to a 6-inch gap between the eyes, when concentrating on a single image, the image appears slightly different to each eye.

A super multi-view (SMV) system with comfortable 3-D effects
Naturally, the human eye vergence and accommodation synchronize with each other which ensures the appearance of an undistorted image in front of the eyes. An Artificial 3D pictures manipulates the vergence-accommodation relation by imitating the natural viewing process. Though they tend to change the vergence distance in a 3D landscape, the eye accommodation distance remains constant, raising eye irritation and discomfort.
Liu explained that the current 3D systems give an output of some views of the displayed spatial spot to a single eye pupil. Due to such an operation, the accommodation distance neglects the key phenomenon in order to adjust with the vergence distance. The team came up with a solution, in which they would provide two viewpoints to the pupil. The team designed a prototype having 11 elementary projecting units, each of which boasts of organic light-emitting diode (OLED) micro display, a rectangular projecting lens, two vertical baffles and a pile of gating apertures (liquid crystal panel) attached to the projecting lens. Adjusting the gating apertures with a corresponding micro display results in dense viewpoints on the display screen.
Liu asserted that the main strength of their project is its applicability in thin structures and its prospective vast scope to emerge as a replacement to modern screen technology in smart wearables. The detailed report of this project was published in the journal Optics Express, from The Optical Society (OSA).
Source: #-Link-Snipped-#
0
