Goal-based Imitation Learning Through Crowdsourcing Helps Robots Learn Faster
@sharvari-panchbhai-JOvYc6
•
Oct 12, 2024
Oct 12, 2024
1.2K
A team from University of Washington researchers, led by Maya Cakmak and Rajesh P. N. Rao, has developed a new way of Goal-based Imitation Learning. The computer scientists have shown how a robot can efficiently complete the task through crowdsourcing. The robot can learn by imitating a human to perform a particular task but it will take a considerable amount of time as the robot in the study uses machine-learning techniques. However, according to the team, a lot of time could be saved if the robot could learn basic steps of the particular task and then take the help of online community for collecting additional input to complete that task efficiently.
To begin the study, the participants built simple models of colored lego blocks like car, turtle, snake, person, etc. When the robot was asked to build a similar model based on few examples, the robot was unable to build the complete model. Here comes the crowdsourcing into picture. The robot was then programmed to take additional input about building the objects from crowdsourcing site. The team hired people on Amazon Mechanical Turk - a crowdsourcing site to build similar models. The robot then researched on more than hundred crowd generated models of each shape based on difficulty to construct and then built models of each participant’s shape. If the goal was to build a person then the result was still a person which was appropriate enough to the original model. Thus, the robot develops the ability to deduce what the human operators want and this ability helps the robot to achieve goals with the best possible way within the stipulated time.
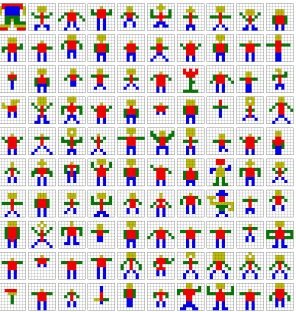
Crowdsourced designs of the word person
In June, the team presented the results of the research at the 2014 Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2014) in Hong Kong. The team has applied the same idea to teach actions to two-armed robots. They physically demonstrated actions to the robot using interactive visualizations of the action. In November, the team will present their work at Conference on Human Computation and Crowdsourcing. The U.S. Office of Naval Research and the National Science Foundation funded this research.
To know more about the research you can have a look at the research paper titled "#-Link-Snipped-#" which was published in ICRA 2014.
Source: <a href="https://www.washington.edu/news/2014/06/26/ask-the-crowd-robots-learn-faster-better-with-online-helpers/" target="_blank" rel="nofollow noopener noreferrer">Ask the crowd: Robots learn faster, better with online helpers | UW News</a>
To begin the study, the participants built simple models of colored lego blocks like car, turtle, snake, person, etc. When the robot was asked to build a similar model based on few examples, the robot was unable to build the complete model. Here comes the crowdsourcing into picture. The robot was then programmed to take additional input about building the objects from crowdsourcing site. The team hired people on Amazon Mechanical Turk - a crowdsourcing site to build similar models. The robot then researched on more than hundred crowd generated models of each shape based on difficulty to construct and then built models of each participant’s shape. If the goal was to build a person then the result was still a person which was appropriate enough to the original model. Thus, the robot develops the ability to deduce what the human operators want and this ability helps the robot to achieve goals with the best possible way within the stipulated time.
Crowdsourced designs of the word person
In June, the team presented the results of the research at the 2014 Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2014) in Hong Kong. The team has applied the same idea to teach actions to two-armed robots. They physically demonstrated actions to the robot using interactive visualizations of the action. In November, the team will present their work at Conference on Human Computation and Crowdsourcing. The U.S. Office of Naval Research and the National Science Foundation funded this research.
To know more about the research you can have a look at the research paper titled "#-Link-Snipped-#" which was published in ICRA 2014.
Source: <a href="https://www.washington.edu/news/2014/06/26/ask-the-crowd-robots-learn-faster-better-with-online-helpers/" target="_blank" rel="nofollow noopener noreferrer">Ask the crowd: Robots learn faster, better with online helpers | UW News</a>
