Desalination Of Sea Water Now Possible With New Sodium-Ion Battery Technology
@raagavan-sivaraja-mBq7hN
•
Oct 26, 2024
Oct 26, 2024
1.9K
A team of researchers at the University of Illinois have formulated a new battery design that will separate salt from sea-water, making it suitable for consumption. In addition to that, this battery uses salt water to store and supply electricity, so it acts both as a battery and as a desalination device. When tried with water that had salt levels equal to sea water, the researchers were able to recover about 80% of the desalinated water. If put into production, this technology could serve drinking water for all, at the expense of very little energy.
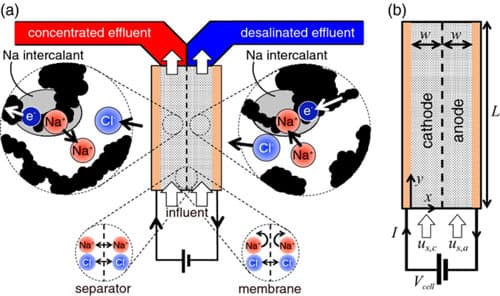
Professor of mechanical science and engineering, Kyle Smith, and his student Rylan Dmello are the researchers behind this discovery, and their findings have been published in the Journal of the Electrochemical Society. Conventionally, desalination was achieved by a process called reverse osmosis, in which the salty sea-water is forced through a membrane that filters the salt, and allows only pure water to pass through. But this method is not scalable as it consumes a lot of energy, and is expensive.

Meanwhile, battery technology has also been evolving and has seen some notable advancements like the Lithium-ion and Sodium-ion batteries. It is Sodium-ion batteries that sparked the idea for these researchers because they contain salt water. When these batteries discharge, the Sodium and Chloride ions are reserved to one of the two chambers, while the other chamber contains purified water.
Usually when the battery charges again, the two ions are diffused into the water again. But Kyle and Rylan have found a way to prevent that. They introduced a membrane between the two chambers that prevents the Sodium from passing through to the desalinated water.
Compared to conventional reverse osmosis apparatus, this battery has a lot of advantages. It need not be as big, and doesn’t consume as much energy as reverse osmosis. It is therefore extremely cost-efficient and compact. Though this mechanism is very promising, the impurities found in sea-water might alter the results of the experiment. The scientists are on to that and are hopeful that their research will open up new avenues in Sodium-ion battery technology in addition to purification of sea-water.
Source: #-Link-Snipped-#

Professor of mechanical science and engineering, Kyle Smith, and his student Rylan Dmello are the researchers behind this discovery, and their findings have been published in the Journal of the Electrochemical Society. Conventionally, desalination was achieved by a process called reverse osmosis, in which the salty sea-water is forced through a membrane that filters the salt, and allows only pure water to pass through. But this method is not scalable as it consumes a lot of energy, and is expensive.

Meanwhile, battery technology has also been evolving and has seen some notable advancements like the Lithium-ion and Sodium-ion batteries. It is Sodium-ion batteries that sparked the idea for these researchers because they contain salt water. When these batteries discharge, the Sodium and Chloride ions are reserved to one of the two chambers, while the other chamber contains purified water.
Usually when the battery charges again, the two ions are diffused into the water again. But Kyle and Rylan have found a way to prevent that. They introduced a membrane between the two chambers that prevents the Sodium from passing through to the desalinated water.
Compared to conventional reverse osmosis apparatus, this battery has a lot of advantages. It need not be as big, and doesn’t consume as much energy as reverse osmosis. It is therefore extremely cost-efficient and compact. Though this mechanism is very promising, the impurities found in sea-water might alter the results of the experiment. The scientists are on to that and are hopeful that their research will open up new avenues in Sodium-ion battery technology in addition to purification of sea-water.
Source: #-Link-Snipped-#

