Fujitsu Brings Liquid Cooling To Smartphones
Fujitsu has announced an innovative liquid cooling heat pipe that can be deployed in compact electronic devices like smartphones or tablets. Liquid cooling systems have existed for desktop class personal computers, but reducing their size to make them fit in tiny gadgets had been a major challenge. The engineering team at Fujitsu has developed a loop heat pipe that's just 1mm thick - and can be accommodated in your smartphone.
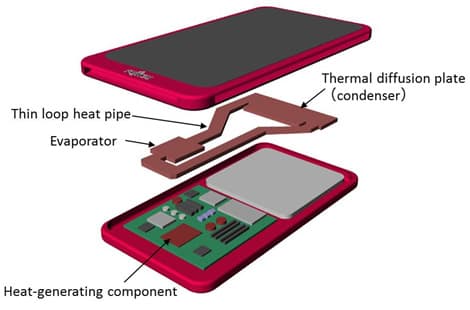
Image Credit: Fujitsu
The modern processors are required to churn out large amounts of data and that leads to greater amount of heat dissipation. This heat dissipation often leads to localised heating of electronic devices. You might have experienced your phone getting warmer after several minutes of graphics-intensive gameplay. Fujitsu engineers have offered to fix this problem with a miniature heat-pipe that can transfer 5x more heat than current heat pipes. Here's a quick look at how this new heat pipe functions -
The Fujitsu miniature heat pipe is a closed system comprising of an evaporator and a condenser. The evaporator will sit closer to a hot spot (CPU or GPU) and the condenser would be located at a relatively cooler section of the phone. Tiny pipes will connect the two to form a closed loop (refer to the image below). The evaporator has six perforated sheets of copper, each about 0.1mm thick. The heat from the hotspot causes the liquid to vaporise and the vapor line will carry these vapors to the condenser where the lower temperature causes the vapours to condense back to liquid state and release heat energy in the process. The liquid moves in the system through capillary action which makes the orientation of the smartphone irrelevant.
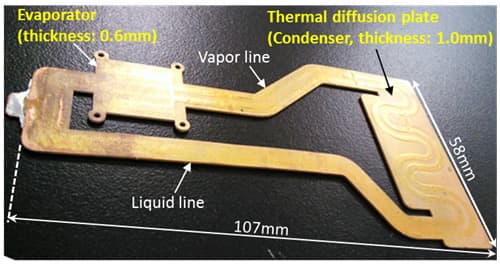
Image Credit: Fujitsu
Read more about the system on official Fujitsu press release linked in the source below. Do let us know your thoughts and ideas on how this system can be improved. We look forward to your ideas.
Source: <a href="https://www.fujitsu.com/global/about/resources/news/press-releases/2015/0312-01.html" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">Fujitsu Develops Thin Cooling Device for Compact Electronics - Fujitsu Global</a>

Image Credit: Fujitsu
The modern processors are required to churn out large amounts of data and that leads to greater amount of heat dissipation. This heat dissipation often leads to localised heating of electronic devices. You might have experienced your phone getting warmer after several minutes of graphics-intensive gameplay. Fujitsu engineers have offered to fix this problem with a miniature heat-pipe that can transfer 5x more heat than current heat pipes. Here's a quick look at how this new heat pipe functions -
The Fujitsu miniature heat pipe is a closed system comprising of an evaporator and a condenser. The evaporator will sit closer to a hot spot (CPU or GPU) and the condenser would be located at a relatively cooler section of the phone. Tiny pipes will connect the two to form a closed loop (refer to the image below). The evaporator has six perforated sheets of copper, each about 0.1mm thick. The heat from the hotspot causes the liquid to vaporise and the vapor line will carry these vapors to the condenser where the lower temperature causes the vapours to condense back to liquid state and release heat energy in the process. The liquid moves in the system through capillary action which makes the orientation of the smartphone irrelevant.

Image Credit: Fujitsu
Source: <a href="https://www.fujitsu.com/global/about/resources/news/press-releases/2015/0312-01.html" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">Fujitsu Develops Thin Cooling Device for Compact Electronics - Fujitsu Global</a>
0
