Design and analysis of Rocket Nozzle
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF SPACE SHUTTLE NOZZLE
ABSTRACT: The function of a rocket nozzle is to channelise and accelerate the combustion products produced by the burning propellant, inside a rocket motor, in such as way so as to maximize the velocity of the exhaust at the exit, to supersonic velocity. The nozzle converts the chemical energy of the propellant into kinetic energy with no moving parts. It is basically a tube with variable cross-sectional area.
Nozzles are generally used to control the rate of flow, speed, direction, mass, shape, and/or the pressure of the exhaust stream that emerges from them. The nozzle is used to convert the chemical-thermal energy generated in the combustion chamber into kinetic energy. The nozzle converts the low velocity, high pressure, high temperature gas in the combustion chamber into high velocity gas of lower pressure and temperature, thus producing the required thrust for the rocket to propel.
The convergent and divergent type of nozzle is known as DE-LAVAL nozzle. Throat is the portion with minimum area in a convergent-divergent nozzle. The divergent part of the nozzle is known as nozzle exit. In the convergent section the pressure of the exhaust gases will increase and as the hot gases expand through the diverging section attaining high velocities from continuity equation.
The analysis of a rocket nozzle involves the concept of "steady, one-dimensional compressible fluid flow of an ideal gas". The goal of rocket nozzle design is to accelerate the combustion products to as high an exit velocity as possible. This is achieved by designing the necessary nozzle geometric profile with the condition that isentropic flow is to be aimed for. Isentropic flow is considered to be flow that is dependant only upon cross-sectional area -- which necessitates frictionless and adiabatic (no heat loss) flow. Therefore, in the actual nozzle, it is necessary to minimize frictional effects, flow disturbances and conditions that can lead to shock losses. In addition, heat transfer losses are to be minimized. In this way, the properties of the flow are near isentropic, and are simply affected only by the changing cross-sectional area as the fluid moves through the nozzle.
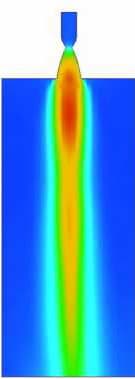
Space shuttle uses some of the largest De-Laval nozzles in the Solid Rocket Boosters(SRBs). They are designed so as to optimize the weight and the performance. In this project a study is conducted to study the various configurations and geometries of a De-laval nozzle w.r.t the available technologies been used in the world. Further an effort is made to analyse the flow of gases through a Space shuttle nozzle using commercially available software.
ABSTRACT: The function of a rocket nozzle is to channelise and accelerate the combustion products produced by the burning propellant, inside a rocket motor, in such as way so as to maximize the velocity of the exhaust at the exit, to supersonic velocity. The nozzle converts the chemical energy of the propellant into kinetic energy with no moving parts. It is basically a tube with variable cross-sectional area.
Nozzles are generally used to control the rate of flow, speed, direction, mass, shape, and/or the pressure of the exhaust stream that emerges from them. The nozzle is used to convert the chemical-thermal energy generated in the combustion chamber into kinetic energy. The nozzle converts the low velocity, high pressure, high temperature gas in the combustion chamber into high velocity gas of lower pressure and temperature, thus producing the required thrust for the rocket to propel.
The convergent and divergent type of nozzle is known as DE-LAVAL nozzle. Throat is the portion with minimum area in a convergent-divergent nozzle. The divergent part of the nozzle is known as nozzle exit. In the convergent section the pressure of the exhaust gases will increase and as the hot gases expand through the diverging section attaining high velocities from continuity equation.
The analysis of a rocket nozzle involves the concept of "steady, one-dimensional compressible fluid flow of an ideal gas". The goal of rocket nozzle design is to accelerate the combustion products to as high an exit velocity as possible. This is achieved by designing the necessary nozzle geometric profile with the condition that isentropic flow is to be aimed for. Isentropic flow is considered to be flow that is dependant only upon cross-sectional area -- which necessitates frictionless and adiabatic (no heat loss) flow. Therefore, in the actual nozzle, it is necessary to minimize frictional effects, flow disturbances and conditions that can lead to shock losses. In addition, heat transfer losses are to be minimized. In this way, the properties of the flow are near isentropic, and are simply affected only by the changing cross-sectional area as the fluid moves through the nozzle.
Space shuttle uses some of the largest De-Laval nozzles in the Solid Rocket Boosters(SRBs). They are designed so as to optimize the weight and the performance. In this project a study is conducted to study the various configurations and geometries of a De-laval nozzle w.r.t the available technologies been used in the world. Further an effort is made to analyse the flow of gases through a Space shuttle nozzle using commercially available software.
0