Electronic switch
I have a basic doubt in a transistor acting as a switch. To switch a lamp, while using a mechanical switch, when we want the lamp to burn we can keep the switch in the ON position and keep the lamp burning as long as we want it to burn and when we don't, we can bring it to OFF position.
But in the case of a transistor used as a switch, since we apply a pulse wave to the base of the transistor, will not the transistor keep on turning on and turning off continuously with the frequency of the applied pulse? Then what is the advantage of using it in the place of a conventional swithch? Or, only in some specail situations do we use it? In that case, what are those situations?
But in the case of a transistor used as a switch, since we apply a pulse wave to the base of the transistor, will not the transistor keep on turning on and turning off continuously with the frequency of the applied pulse? Then what is the advantage of using it in the place of a conventional swithch? Or, only in some specail situations do we use it? In that case, what are those situations?
Replies
-
 reachrkataSimplest and straightforward answer - An electronic switch eliminates Human intervention i.e you can write a program to turn on and off an electronic switch, but you would still have to go and push the mechanical switch on and off manually.
reachrkataSimplest and straightforward answer - An electronic switch eliminates Human intervention i.e you can write a program to turn on and off an electronic switch, but you would still have to go and push the mechanical switch on and off manually.
-Karthik -
 ananthuu
ananthuu
Thank you. Does it mean that the transistors are emplyed as a switch in circuits which requires repeated turning on and turning off ? I will be more enlightened if you give me a specific example. Also, is it correct to say that an electronic switch will be of no practical use in domestic wirings where we require the ON and OFF only arbitrarily?reachrkataSimplest and straightforward answer - An electronic switch eliminates Human intervention i.e you can write a program to turn on and off an electronic switch, but you would still have to go and push the mechanical switch on and off manually.
-Karthik -
 reachrkataRepeated on-off is just one of the scenarios.
reachrkataRepeated on-off is just one of the scenarios.
Another typical application would be to switch off/on something based on a special condition (like temperature) which a person cannot be continuously monitoring. Better let the electronics take care of it !!
-Karthik -
 vishnu tejThese transistor switches can be used for controlling high power devices such as motors, solenoids or lamps, but they can also used in digital electronics and logic gate circuits.
vishnu tejThese transistor switches can be used for controlling high power devices such as motors, solenoids or lamps, but they can also used in digital electronics and logic gate circuits.
If the circuit uses the Bipolar Transistor as a Switch, then the biasing of the transistor, either NPN or PNP is arranged to operate the transistor at both sides of the “ I-V ” characteristics curves we have seen previously.
The areas of operation for a Transistor Switch are known as the Saturation Region and the Cut-off Region. This means then that we can ignore the operating Q-point biasing and voltage divider circuitry required for amplification, and use the transistor as a switch by driving it back and forth between its “fully-OFF” (cut-off) and “fully-ON” (saturation) regions as shown below.
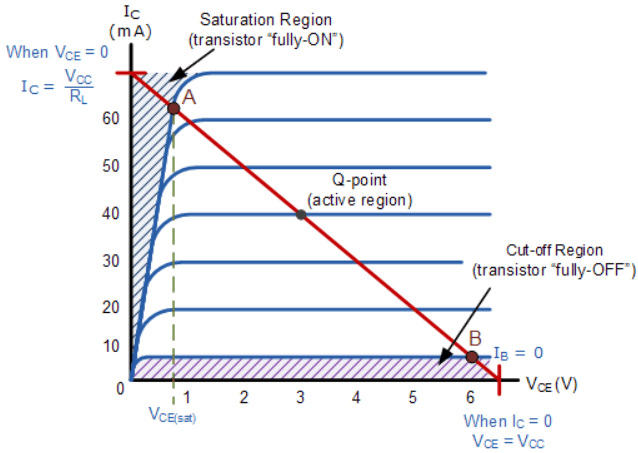
The pink shaded area at the bottom of the curves represents the “Cut-off” region while the blue area to the left represents the “Saturation” region of the transistor.
For application purpose, we can make use of these two regions only.
You are reading an archived discussion.
Related Posts
hi........i am ec student....
i want to make a transformer which can be work at 3 MHz frequency.....
primary voltage of 60v and secondary voltage of 12 v nd secondary...
... with many of us not realizing the importance of water, I think we have moon to look upon for our future water needs. Ah! does it mean we mean...
Link: Know Your CEan - CrazyEngineers
Discuss the interview in this thread 😀
Let's compile the best salary negotiation tips. Will come handy when you are negotiating your salary with your new employers.
Here's my tip:
Never disclose how much you expect from...
Most of you might have seen 2012 movie by now. Can someone post a review for the rest of us? 😀
