Robotic Arms Could Potentially Be Used To Perform 'Soft Tissue' Surgery
Engineering science, blended with medical diagnostics and surgery have proved to be an integral part of contemporary society. Although nothing new, old information regarding such a collaboration is ready to get an update with constant improvement in the fields of research and development.
Researchers at the premier Johns Hopkins University have innovated a robotic arm which will ease the surgeons' workload by accurately operating “soft tissues†during a surgery. The assigned team explained how they had realised the idea of an autonomous robotic surgeon to remove the slightest errors that can creep in, if operations are performed using human effort.
Simon Leonard, from the John Hopkins Whiting School of Engineering, along with five co-authors have worked together for four years, to optimize the electronic arm for stitching soft tissues without any external impulses effecting the subject. Robots have been previously implemented in surgeries involving bones, but that was comparatively easier as gripping bones require much less attention than stitching soft tissues.
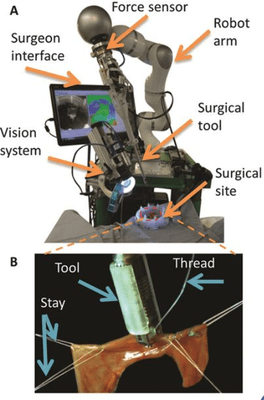
Automating soft tissue surgery
Soft tissues behave in a complex manner which adapts to external stimuli, while the operation in running. To acclimatize with such factors, a human mind was a prior requirement which would now be potentially replaced by pre programmed software. The University press release claims that 44.5 million soft-tissue surgeries take place every year in the United States. Scientists took two different approaches, among which the first was intended for anastomosis, a phenomenon to join two tubular structures such as blood vessels.
Patients who suffer from such after effects could draw enormous benefits from the latest research. The developed prototype named Smart Tissue Autonomous Robot (STAR) comprises a 3D imaging system and a near-infrared sensor to spot fluorescent markers corresponding to a tissue-edge to fix the robotic stature-needle, just at the calculated space.
The results were compared to 5 different doctors on the basis of open, laproscopic and robot-assisted methods. Eliminating all scepticism, almost all the results were either at par or surpassed that of surgeons. The report explaining their research was published in the Science Translational Medicine journal.
Journal : #-Link-Snipped-# | #-Link-Snipped-#
Researchers at the premier Johns Hopkins University have innovated a robotic arm which will ease the surgeons' workload by accurately operating “soft tissues†during a surgery. The assigned team explained how they had realised the idea of an autonomous robotic surgeon to remove the slightest errors that can creep in, if operations are performed using human effort.
Simon Leonard, from the John Hopkins Whiting School of Engineering, along with five co-authors have worked together for four years, to optimize the electronic arm for stitching soft tissues without any external impulses effecting the subject. Robots have been previously implemented in surgeries involving bones, but that was comparatively easier as gripping bones require much less attention than stitching soft tissues.

Automating soft tissue surgery
Patients who suffer from such after effects could draw enormous benefits from the latest research. The developed prototype named Smart Tissue Autonomous Robot (STAR) comprises a 3D imaging system and a near-infrared sensor to spot fluorescent markers corresponding to a tissue-edge to fix the robotic stature-needle, just at the calculated space.
The results were compared to 5 different doctors on the basis of open, laproscopic and robot-assisted methods. Eliminating all scepticism, almost all the results were either at par or surpassed that of surgeons. The report explaining their research was published in the Science Translational Medicine journal.
Journal : #-Link-Snipped-# | #-Link-Snipped-#
Replies
-
 swethathomasNow it is known to me that articles is nothing but inspiring is everything to do something great. This is a great article for the people who want to come in freelancing.
swethathomasNow it is known to me that articles is nothing but inspiring is everything to do something great. This is a great article for the people who want to come in freelancing.
#-Link-Snipped-#
You are reading an archived discussion.
Related Posts
Hello sir, I really need your help right now ... I've researched many IT courses like Java, oracle, php, software testing, ruby, python and many more... Sir plz help me...
Hi,
I am asking this question from the context of subnets and subnetting.
I read an article that uses block size to determine the number of valid subnets. The idea...
Hello friends,
What inference can be drawn from the statement "we cannot assign network ID and broadcast address to a host".
In what context is the author talking about?
Quote:
Car manufacturers love to show off their futuristic car designs. Some of these innovative features are even incorporated into soon-to-be-released models. Other concepts may not be seen in production...
I m confused about my aim. while i think a lot. finaly it comes into my mind to startup but i haven't any knowledge about how start actually. From where...
