UW Engineers Develop Pen-Sized Microscope That Can Detect Cancer Cells
In an amazing breakthrough, engineers from University of Washington have developed a miniature handheld microscope that could help doctors and dentists distinguish between healthy and cancerous cells in an office setting or operating room. It acquires special significance in brain tumor operations in Neuro-surgery, where there is no time to send samples for biological examination at pathology labs once a surgeon cracks open the skull. The surgeons normally rely on subjective senses of their sight, touch and pre-operative images of the brain to gauge such operations. But with this new device, they can now “see†at a cellular level in the operating room as there are often cells left behind that are invisible to the neurosurgeon and determine exactly how much further the residual tissue needs to be reduced.
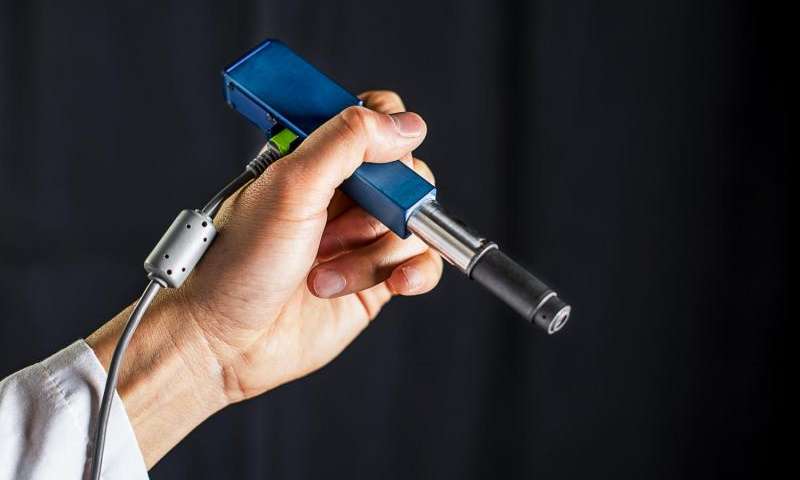

The device can also prove to be of immense benefit for dentists, who spotting a suspicious-looking lesion in a patient’s mouth often wind up cutting it out and sending it to a lab to be biopsied for oral cancer. Most of them are diagnosed to be benign. The device could be used to detect changes at a cellular level in dental or dermatological clinics to better assess which lesions or moles are normal and which ones need to be biopsied thereby reducing pressure on pathology laboratories and sparing the patients invasive methodologies.
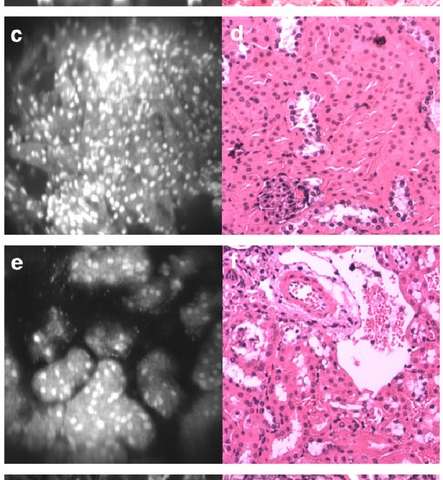
The real-time microscope images (left) illuminate similar details in mouse tissues as the images (right) produced during an expensive, multi-day process at a clinical pathology lab at University of Washington.
The advances in the microscope technologies in preceding couple of decades are expensive and still pretty large, hence there is really a need for creating much more miniaturized microscopes. It could prove to be of much help in rural, small town settings of developing countries where medical infrastructure is not up to the mark, aiding doctors immensely in their work settings.
The research paper is published in journal #-Link-Snipped-#. The researchers hope that after testing the microscope’s performance as a cancer-screening tool in clinical settings next year, it can be introduced into surgeries or other clinical procedures within the next 2 to 4 years.
Source:<a href="https://www.washington.edu/news/2016/01/25/new-handheld-pen-sized-microscope-could-id-cancer-cells-in-doctors-offices-and-operating-rooms/" target="_blank" rel="nofollow noopener noreferrer">New handheld, pen-sized microscope could ID cancer cells in doctor’s offices and operating rooms | UW News</a>

The device can also prove to be of immense benefit for dentists, who spotting a suspicious-looking lesion in a patient’s mouth often wind up cutting it out and sending it to a lab to be biopsied for oral cancer. Most of them are diagnosed to be benign. The device could be used to detect changes at a cellular level in dental or dermatological clinics to better assess which lesions or moles are normal and which ones need to be biopsied thereby reducing pressure on pathology laboratories and sparing the patients invasive methodologies.

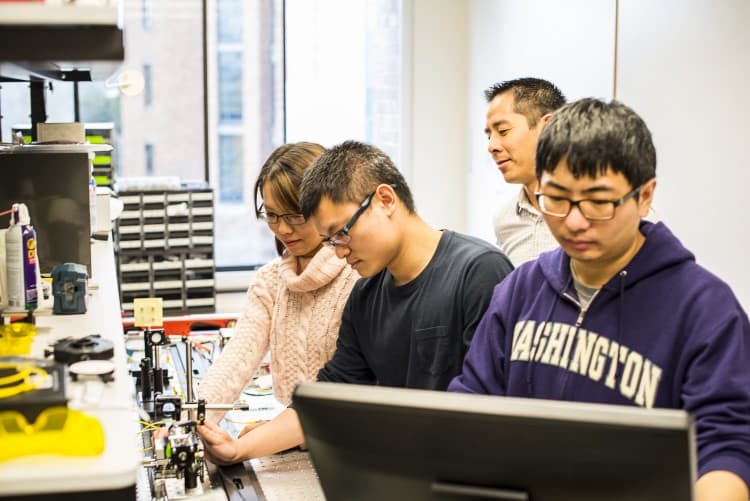
UW mechanical engineering doctoral students and assistant professor Jonathan T.C. Liu work to align a handheld microscope for cancer detection in patients
The miniature microscope uses an innovative approach called “dual-axis confocal microscopy†to illuminate and see more clearly through the opaque tissue. It can effectively capture details up to a half millimeter beneath the tissue surface, where some types of cancerous cells originate. The microscope also employs a technique called line scanning to speed up the image-collection process. It uses micro-electrical-mechanical — also known as MEMS — mirrors to direct an optical beam, scanning tissues in a line and aiding to generate an image quickly.

The real-time microscope images (left) illuminate similar details in mouse tissues as the images (right) produced during an expensive, multi-day process at a clinical pathology lab at University of Washington.
The research paper is published in journal #-Link-Snipped-#. The researchers hope that after testing the microscope’s performance as a cancer-screening tool in clinical settings next year, it can be introduced into surgeries or other clinical procedures within the next 2 to 4 years.
Source:<a href="https://www.washington.edu/news/2016/01/25/new-handheld-pen-sized-microscope-could-id-cancer-cells-in-doctors-offices-and-operating-rooms/" target="_blank" rel="nofollow noopener noreferrer">New handheld, pen-sized microscope could ID cancer cells in doctor’s offices and operating rooms | UW News</a>
0
