Sugar Powered Batteries Can Run Smartphones For 10 Days - Virginia Tech
As smartphones and tablets evolve, they get faster and gain more useful features. However, there is one place where they are still lagging and that is the battery life. Many devices still require daily charging. All cell-phone owners hate to lose their calls due to batteries running out and batteries are not always easy to recharge. Keeping this concept in mind, researchers at Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University have developed a new bio-battery that uses sugar as a fuel and can run your smartphone for 10 days. Sounds great, right? Well this sugar-powered battery is cheap, biodegradable, and powerful enough to run electronic gadgets.
This battery converts sugar into energy in a similar fashion like our metabolism by decomposing sugar into carbon dioxide and water and releasing electrons.Also it completely converts sugar into energy. This means that it generates more power output than previous bio-batteries along with a greater battery charge than common lithium-ion batteries.
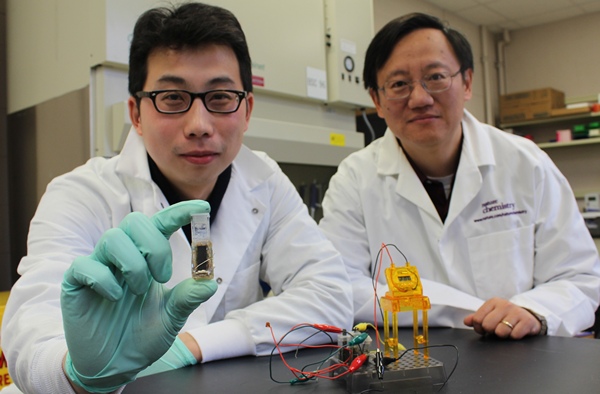
Typically most bio-batteries are unable to generate large amounts of power, but researchers recently developed a prototype version that has the potential to be lighter and more powerful than the batteries usually found in present day's electronic devices, including smartphones. One of the major advantages of this battery is that, it is more robust as it uses lesser number of enzymes to fully convert sugar into energy. Researchers claim that the current battery has low power output for many devices. Also, since it cannot be recharged at this stage hence, the lifetime of the cell is too short. These challenges are on the engineering side which would have to be overcomed before putting these bio-batteries into commercial use.
This research was published in the journal #-Link-Snipped-# by Zhang and Zhiguang Zhu, researchers at Virginia Tech, in Blacksburg. This breakthrough is important not only for mobile computing and telecoms but also for the emerging electric-vehicle market. This research will attract more innovations in this sector resulting in smaller and lighter batteries that will be able to hold more charge for longer period of time. What are your views pertaining to this innovation ? Share your views with us in comment section below.
Source : #-Link-Snipped-#
This battery converts sugar into energy in a similar fashion like our metabolism by decomposing sugar into carbon dioxide and water and releasing electrons.Also it completely converts sugar into energy. This means that it generates more power output than previous bio-batteries along with a greater battery charge than common lithium-ion batteries.
This battery generates its efficiency by using a novel system of enzymes. These are proteins, which act as catalyst in helping the reaction to take place. The system uses two active enzymes that liberate two pairs of electrons from the sugar, while 10 other enzymes help to reset the reaction inside the bio-battery. Once the reaction is reset, the active enzymes release another quartet of electrons. At the end of six cycles, the bio-battery extracts all of the energy from the sugar molecule, along with carbon dioxide and water.

Typically most bio-batteries are unable to generate large amounts of power, but researchers recently developed a prototype version that has the potential to be lighter and more powerful than the batteries usually found in present day's electronic devices, including smartphones. One of the major advantages of this battery is that, it is more robust as it uses lesser number of enzymes to fully convert sugar into energy. Researchers claim that the current battery has low power output for many devices. Also, since it cannot be recharged at this stage hence, the lifetime of the cell is too short. These challenges are on the engineering side which would have to be overcomed before putting these bio-batteries into commercial use.
This research was published in the journal #-Link-Snipped-# by Zhang and Zhiguang Zhu, researchers at Virginia Tech, in Blacksburg. This breakthrough is important not only for mobile computing and telecoms but also for the emerging electric-vehicle market. This research will attract more innovations in this sector resulting in smaller and lighter batteries that will be able to hold more charge for longer period of time. What are your views pertaining to this innovation ? Share your views with us in comment section below.
Source : #-Link-Snipped-#
Replies
You are reading an archived discussion.
Related Posts
Skoda India has launched a special edition of Skoda Rapid Ultima and it has started selling through the company's dealerships from 1st of March, 2014. The sedan will available for...
After dual sim phones stopped being cool, it's the time for smartphones with dual operating system. Karbonn mobile, which is currently the fourth largest company in the handset market, has...
This premium quality paper developed by prominent paper making company named Fedrigoni claims to soon replace the existing leather exterior of the Leica X2 Premium range Cameras. This paper is...
The pro gadget information leaker @evleaks has again outed a news and this time it's about Samsung’s new Chromebook which seems to be its target. According to a report in...
today i saw an induction motor which is connected in delta/star connection to the supply (written on nameplate).generally i have seen nameplates with star/delta. can anyone explain what is the...
