Nanofluids To Prevent Electronics From Overheating - Improve Their Thermal Performance
Electronic devices contain active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, diodes, transistors and integrated circuits along with passive interconnection technologies. While using devices such as computers, mobiles, etc. the users perform lots of tasks. This leads to massive pressure on diminutive elements that whir and generate heat while performing tasks. Many alternatives such as heat sinks and fans for air cooling are used for dissipating heat. Recently, the research team of University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur has demonstrated that the liquid containing nanoparticles has the potential to help the devices stay cool when there is a considerable amount of heat dissipation.
According to the team, during the working of the electronic devices, problems such as power dissipation, chip power consumption, and heat flux arise. Owing to these increasing problems over the past decade, there is a necessity of new improved methods for cooling the electronic devices. To improve the thermal performance of electronic devices, nanofluids were used to carry out the research. The team did the analysis of the energy, exergy (energy that is available for use), and frictional efficiency of different nanofluids that can be helpful in cooling the devices.
The analysis of the nanofluids was done by creating an analytical model. In this model, different nanofluids flowed at a speed of 0.5 m/s through a micro channel heat sink that is rectangular in shape. Heat flux (heat rate per unit area) in the micro channel heat sink was constant. The main content of nanofluids is water as a base fluid and other constituents like aluminium oxide (Al2O3), 0.4 to 2.0 volume % of copper oxide (CuO), and titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles.
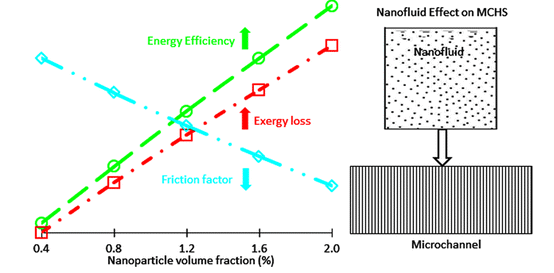
The results proved that as the volume fraction of nanoparticles increases, thermal resistance decreases. Out of the three nanofluids, CuO-water nanofluid had maximum energy efficiency. The energy efficiency of heat sink is directly proportional to the volume fraction of nanoparticles. The energy efficiency of CuO-water ,Al2O3-water, and TiO2-water nanofluids were 98.9% ,77.5% and 68.4%, respectively. And, lowest exergy losses for TiO2-water, Al2O3-water, and CuO-water nanofluids were 19.2 W, 20.9 W, and 25.1W respectively. CuO-water nanofluid was more efficient in minimizing thermal resistance and maximizing the pressure reduction as compared to other two.
The research was funded by the Ministry of Education Malaysia. For more details you can have a look at the research paper which was published in #-Link-Snipped-# Journal.
Source: #-Link-Snipped-#
According to the team, during the working of the electronic devices, problems such as power dissipation, chip power consumption, and heat flux arise. Owing to these increasing problems over the past decade, there is a necessity of new improved methods for cooling the electronic devices. To improve the thermal performance of electronic devices, nanofluids were used to carry out the research. The team did the analysis of the energy, exergy (energy that is available for use), and frictional efficiency of different nanofluids that can be helpful in cooling the devices.
The analysis of the nanofluids was done by creating an analytical model. In this model, different nanofluids flowed at a speed of 0.5 m/s through a micro channel heat sink that is rectangular in shape. Heat flux (heat rate per unit area) in the micro channel heat sink was constant. The main content of nanofluids is water as a base fluid and other constituents like aluminium oxide (Al2O3), 0.4 to 2.0 volume % of copper oxide (CuO), and titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles.
The results proved that as the volume fraction of nanoparticles increases, thermal resistance decreases. Out of the three nanofluids, CuO-water nanofluid had maximum energy efficiency. The energy efficiency of heat sink is directly proportional to the volume fraction of nanoparticles. The energy efficiency of CuO-water ,Al2O3-water, and TiO2-water nanofluids were 98.9% ,77.5% and 68.4%, respectively. And, lowest exergy losses for TiO2-water, Al2O3-water, and CuO-water nanofluids were 19.2 W, 20.9 W, and 25.1W respectively. CuO-water nanofluid was more efficient in minimizing thermal resistance and maximizing the pressure reduction as compared to other two.
The research was funded by the Ministry of Education Malaysia. For more details you can have a look at the research paper which was published in #-Link-Snipped-# Journal.
Source: #-Link-Snipped-#
Replies
You are reading an archived discussion.
Related Posts
I was awoken by a certain SMS today morning which was from BV-BSNLCare saying
Dear Customer, Your Broadband Usage with ID xxxxxx has reached 100 Percent of your Free Usage....
Nanobi Analyitcs is a Bangalore based data and analytics startup founded in the year 2012 by Mahesh Ramakrishnan.
The Founder and CEO at Nanobi Analytics, Mahesh Ramakrishnan holds a B.E....
JEE Main 2014 Result is released by Central Board of Secondary Education every year for the candidates those who appeared in the examination. The result shows the performance of the...
Hello peeps,
Just completed Electrical And Electronics Engineering with a cgpa of 6.5 (i know its low but that's all i could manage 😔 ). Am confused on what to...
It's France Vs. Germany at FIFA 2014 today and we're just about 25 minutes away from the official war. I'm sure all our CEans must have taken their sides with...
