German Researchers Find Security Flaw In Thousands of Popular Apps
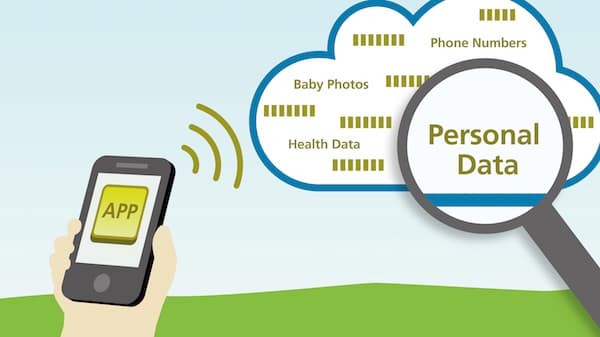
Scientists at the Darmstadt University of Technology and Fraunhofer Institute for Secure Information Technology, Germany have found a major bug in thousands of popular app in Apple iTunes Store and Google Play Store. The security flaw has the potential of letting an attacker access sensitive personal information of users. This information can include passwords, current location as well as usernames, photos, videos, health records, monetary transactions and office/home addresses. These apps belonging to every category from gaming to messaging, social networking to bankings and fitness to medical & healthcare apps have ~ 56 million items of data left unprotected from hackers/attackers. Prof. Eric Bodden, Ph.D., Head of Secure Software Engineering at Fraunhofer SIT and TU Darmstadt, who led this research team believes that if an attack is made using this security flaw billions of app users would be affected.
At first, the attention was focused to this problem when Fraunhofer SIT was alerted by a student, Robert Hahn, who had been looking to use one of the BaaS (Backend-as-a-Service) interfaces in a mobile application. The security researchers investigated cloud databases such as Facebook’s Parse and Amazon's AWS, services that are used by app developers to upload, download & backup the user's data. While doing this, many developers use one of the weakest forms of authentication called API-tokens. It is an alphanumeric code that gets embedded in the app's code. However, with current technology and tools available, attackers are able to extract these tokens to easily read & manipulate the data stored. An attacker could build a botnet, blackmail an user, deform a website or simply spread malware with power & control over user's personal information
What can developers do to address this issue?
The German researchers suggest that app developers implement an access-control scheme. They should again read the security documentation available from BaaS providers and append sensible access control over their apps. For instance, AWS users can authenticating users of AWS mobile apps with a Token Vending Machine or create temporary security credentials using identity providers.
The Fraunhofer SIT team could not reveal the data about the app names that have this security flaw because German and EU law currently does not allow distribution of product warnings.
However, they have gone ahead and informed the respective app developers about the danger and requested them to take necessary action without underestimating its effects.
The researchers have equated the magnanimity of the app vulnerability to the Heartbleed Bug: Public urged to reset all passwords that was found last year and have warned that millions can be affected.
What are your thoughts about saving your personal information on third party apps and such a serious security flaw? Share with us in comments below.
Source: #-Link-Snipped-#
At first, the attention was focused to this problem when Fraunhofer SIT was alerted by a student, Robert Hahn, who had been looking to use one of the BaaS (Backend-as-a-Service) interfaces in a mobile application. The security researchers investigated cloud databases such as Facebook’s Parse and Amazon's AWS, services that are used by app developers to upload, download & backup the user's data. While doing this, many developers use one of the weakest forms of authentication called API-tokens. It is an alphanumeric code that gets embedded in the app's code. However, with current technology and tools available, attackers are able to extract these tokens to easily read & manipulate the data stored. An attacker could build a botnet, blackmail an user, deform a website or simply spread malware with power & control over user's personal information

What can developers do to address this issue?
The German researchers suggest that app developers implement an access-control scheme. They should again read the security documentation available from BaaS providers and append sensible access control over their apps. For instance, AWS users can authenticating users of AWS mobile apps with a Token Vending Machine or create temporary security credentials using identity providers.
The Fraunhofer SIT team could not reveal the data about the app names that have this security flaw because German and EU law currently does not allow distribution of product warnings.
However, they have gone ahead and informed the respective app developers about the danger and requested them to take necessary action without underestimating its effects.
The researchers have equated the magnanimity of the app vulnerability to the Heartbleed Bug: Public urged to reset all passwords that was found last year and have warned that millions can be affected.
What are your thoughts about saving your personal information on third party apps and such a serious security flaw? Share with us in comments below.
Source: #-Link-Snipped-#
Replies
You are reading an archived discussion.
Related Posts
For the disgustingly rich. All Rajas, Lalits can head there. Sorry, only by invitation.
Quote:
It never hurts to be prepared for the unexpected — like say, an all-out zombie...
Mega Engineering!
https://worldindustrialreporter.com/...he-worlds-largest-cargo-ship/?adsrc_=promofun
Hi,
Does anyone know some good institutes in Pune or Bengaluru (or other cities in India) that offer industry level certifications or training in PCB designing for students with BE...
The latest fashion among all the startups that are in the ideation or very early stage with products in stealth mode is to get incubated. I've even known startups that...
Indian phone brand Micromax has unveiled the all new Micromax Canvas Silver 5. Priced at Rs. 17,999, the phone is claiming to be the world's thinnest and lightest phone ever!...
