Flexible Electronic Material From Penn State University Can Heal Itself When Cut In Half
Wearables are the next big thing in technology but the creations we have seen so far implement electronics from the present generation which cannot bend or contour with our body which makes them bulky and cumbersome to use on a daily basis. Even if wearables use flexible electronic material they are not strong enough to cope with daily wear and tear and once broken they cannot be put together again. Researchers from the Penn State University have come to the rescue by creating a flexible electronic material that is capable of healing itself and can work like before even after multiple breaks.
Researchers at the Penn State University led by professor of materials science and engineering, Qing Wang wanted to create a flexible material that would be perfect for wearable and bendable electronics. While the researchers are keeping details about the composition of the material close to their chest they are willing to discuss the advantages of their material. While other self healing materials are soft or gum-like the material created by Wang and his team is tougher in comparison. They added boron nitride nanosheets to a base material of plastic polymer. They chose boron nitride nanosheets instead of graphene which is also two dimensional because instead of conducting electricity like graphene the boron nitride nanosheets resist and insulate it making the material dielectric.
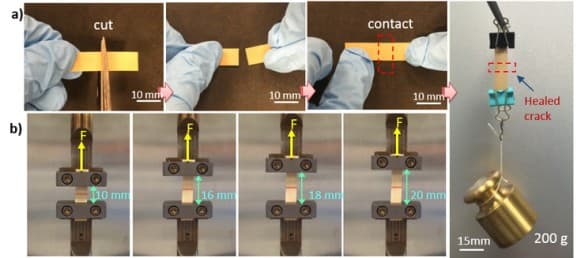
As you can see in the picture above, the researchers at the Penn State University cut the electronic material in half and then rejoined it for it to heal. Once the material is healed it is able to stretch and also able to hold a small weight. The material is able to heal itself because of the same boron nitride nanosheets we talked about earlier. When a disjoined pair is held together the electrostatic attraction between hydrogen bonding groups is restored and the two pieces are joined together. Another advantage of using boron nitride nanosheets is that they are resistant to moisture which means they can withstand high humidity and the occasional splash of water.
The team have published their findings on the Advanced Functional Materials journal online and you can read more about their creation on #-Link-Snipped-#.
Researchers at the Penn State University led by professor of materials science and engineering, Qing Wang wanted to create a flexible material that would be perfect for wearable and bendable electronics. While the researchers are keeping details about the composition of the material close to their chest they are willing to discuss the advantages of their material. While other self healing materials are soft or gum-like the material created by Wang and his team is tougher in comparison. They added boron nitride nanosheets to a base material of plastic polymer. They chose boron nitride nanosheets instead of graphene which is also two dimensional because instead of conducting electricity like graphene the boron nitride nanosheets resist and insulate it making the material dielectric.

As you can see in the picture above, the researchers at the Penn State University cut the electronic material in half and then rejoined it for it to heal. Once the material is healed it is able to stretch and also able to hold a small weight. The material is able to heal itself because of the same boron nitride nanosheets we talked about earlier. When a disjoined pair is held together the electrostatic attraction between hydrogen bonding groups is restored and the two pieces are joined together. Another advantage of using boron nitride nanosheets is that they are resistant to moisture which means they can withstand high humidity and the occasional splash of water.
The team have published their findings on the Advanced Functional Materials journal online and you can read more about their creation on #-Link-Snipped-#.
Replies
You are reading an archived discussion.
Related Posts
Alcatel telecom brand, the TCL corporation's spin-off has recently launched its Pop series' latest smartphone, the "Pop Star" in India. The official debut was set on 23rd may and according...
Are we close to the day when a real life Tony Stark will have to monitor the biochemical reactions inside his body to maintain his brain-body combo as Ironman? Researchers...
Just a couple of days back we witnessed a sensational development in Organic Radical Batteries by Hiroshima University. But due to technical complicacy, such an environment friendly system would take...
ZenFone Max, a new flagship device from the Asus, has recently been launched in India at a price starting from INR 8,999. The device is available for sale in India...
I'm looking for Country / State (Region) / City data in JSON format. I thought I'd easily find a database (or even a web service) that lets me populate the...
