Bladabindi Malware Affecting Windows Computers In India - CERT-In Warns
A new malware that goes by the name 'Bladabindi' has been found to have hit hundreds of computers in India and the Government of India's CERT-In or Computer Emergency Response Team has started warning Indian computer users to beware of it. The Bladabindi virus is capable of stealing sensitive personal information from the victim's computer and sending it to a malicious hacker sitting anywhere across the world. The malware can give backdoor access to your PC in the hands of the hacker. After infecting a single machine, the Bladabindi virus can spread through USB flash drive (pen drives, hard disks) and other removable drives. The computers can also catch on the malware by accidentally downloading other malicious software from malicious links and hacked websites.
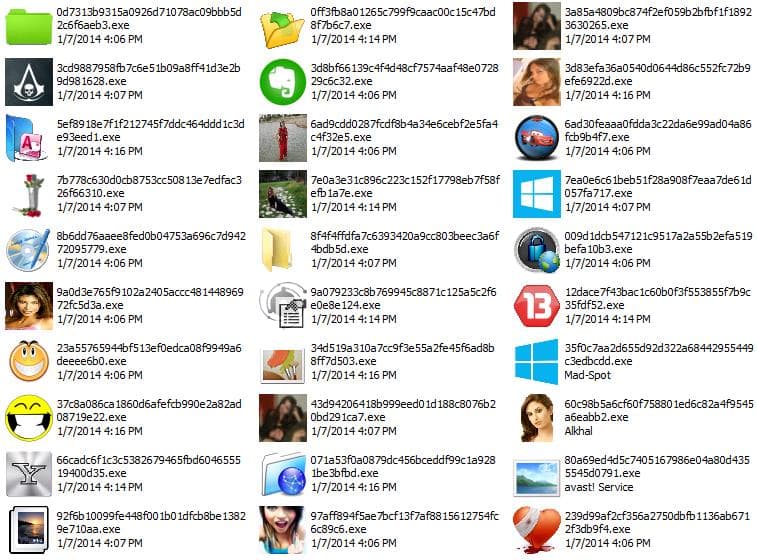
The many variants of Bladabindi virus are also capable of capturing the computer's web camera, control the keyboard press, steal passwords stored in internet browsers such as Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome or Opera and store DynDNS and No-IP/DUC information too. In fact, the CERT-In team has found 13 different version of the new virus, that can harm your machine and steal the data residing in it. Following are some of the sample file icons used by Bladabindi till date -
If users run any of the files mentioned above or others similar to it, the Bladabindi malware will copy itself to one of the locations on your machine with a variable name. For example #-Link-Snipped-#\svhost.exe or #-Link-Snipped-# or #-Link-Snipped-# or #-Link-Snipped-#. It could also change certain specific registry entries so that it runs each time you start your PC. Moreover, the trojan can connect to remote servers to download and install updates or other malware. The Microsoft team has found it connecting to - fox2012.no-ip.org, jn.redirectme.net, moudidz.no-ip.org and reemo.no-ip.biz.
Thankfully, the Microsoft team has acknowledged the presence of this virus and shared some of the preventive measure that Windows OS users can use. Free Microsoft software that detects and removes this threat include - #-Link-Snipped-# for Windows 8.1, or #-Link-Snipped-# for Windows 7 andWindows Vista, #-Link-Snipped-# and #-Link-Snipped-#.
Other than doing regular scans of your computers, the CERT-In team wants users to always apply OS and security fixes as soon as possible, refraining from opening the malicious looking email attachments, disabling the autorun feature on Windows and last but not the least - keep really strong passwords.
Source: #-Link-Snipped-#
The many variants of Bladabindi virus are also capable of capturing the computer's web camera, control the keyboard press, steal passwords stored in internet browsers such as Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome or Opera and store DynDNS and No-IP/DUC information too. In fact, the CERT-In team has found 13 different version of the new virus, that can harm your machine and steal the data residing in it. Following are some of the sample file icons used by Bladabindi till date -

If users run any of the files mentioned above or others similar to it, the Bladabindi malware will copy itself to one of the locations on your machine with a variable name. For example #-Link-Snipped-#\svhost.exe or #-Link-Snipped-# or #-Link-Snipped-# or #-Link-Snipped-#. It could also change certain specific registry entries so that it runs each time you start your PC. Moreover, the trojan can connect to remote servers to download and install updates or other malware. The Microsoft team has found it connecting to - fox2012.no-ip.org, jn.redirectme.net, moudidz.no-ip.org and reemo.no-ip.biz.
Thankfully, the Microsoft team has acknowledged the presence of this virus and shared some of the preventive measure that Windows OS users can use. Free Microsoft software that detects and removes this threat include - #-Link-Snipped-# for Windows 8.1, or #-Link-Snipped-# for Windows 7 andWindows Vista, #-Link-Snipped-# and #-Link-Snipped-#.
Other than doing regular scans of your computers, the CERT-In team wants users to always apply OS and security fixes as soon as possible, refraining from opening the malicious looking email attachments, disabling the autorun feature on Windows and last but not the least - keep really strong passwords.
Source: #-Link-Snipped-#
0
