Bio-Bots Powered By Muscle Cells Developed By University Of Illinois
Taking cue from nature for your next robotics project might be the most sane thing to do. As engineers and researchers from across the globe are developing interesting robots that mimic different animals and birds from nature, a new breed of robotics known as 'bio-bots' has taken to rise. Now a group of engineers from University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have developed “bio-bots†that can walk and are powered by muscle cells and controlled using electrical pulses. In their research of building a biological machine, the team led by Prof. Rashid Bashir, the head of bioengineering at the University, tried to integrate the principles of engineering with biology to design a bio-system that can have environmental and medical applications.
Previously, the team had done a successful demo of walking bio-bots that were powered by rat's beating heart cells. This one suffered from the limitation of not being able to turn on and off or speed up and down. A significant improvement from that project, now smaller than a centimeter in size, the bio-bots are developed using flexible 3-D printed hydrogels living cells.
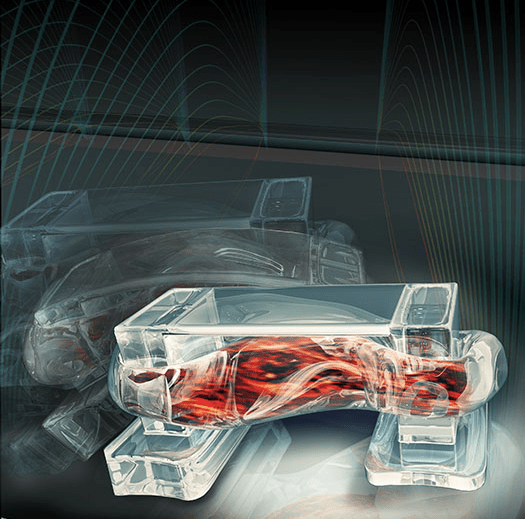
The team's design takes inspiration from the muscle-tendon-bone complex commonly found in nature. This muscle acts as a strong backbone for the 3D printed Hydrogel while remaining flexible enough to bend like a joint. The engineers adjusted the frequency of the electric pulses to control the speed of the bot. The higher the frequency, the faster the muscle contracts. Do take a look at the following video to see the bio-bots in action -
In near future, the possibility of more efficient biological machines that can be stimulated, trained, or programmed to do work, can not be denied and now seems only more probable. In application areas such as delivery of drugs inside human body to smart implants and other surgical robots, the bio-bots prove to be a significant improvement over ongoing research.
The engineering researchers are now busy working on integration of the neurons so the bio-bots can be steered in different directions with light or chemical gradients. 3-D printing has become a major boon for these engineers as creating different shapes and designs has become quick and easy.
We will keep you updated on this research. Till then, let us know what are your thoughts on bio-bots through comments.
Source: #-Link-Snipped-#
Previously, the team had done a successful demo of walking bio-bots that were powered by rat's beating heart cells. This one suffered from the limitation of not being able to turn on and off or speed up and down. A significant improvement from that project, now smaller than a centimeter in size, the bio-bots are developed using flexible 3-D printed hydrogels living cells.

The team's design takes inspiration from the muscle-tendon-bone complex commonly found in nature. This muscle acts as a strong backbone for the 3D printed Hydrogel while remaining flexible enough to bend like a joint. The engineers adjusted the frequency of the electric pulses to control the speed of the bot. The higher the frequency, the faster the muscle contracts. Do take a look at the following video to see the bio-bots in action -
In near future, the possibility of more efficient biological machines that can be stimulated, trained, or programmed to do work, can not be denied and now seems only more probable. In application areas such as delivery of drugs inside human body to smart implants and other surgical robots, the bio-bots prove to be a significant improvement over ongoing research.
The engineering researchers are now busy working on integration of the neurons so the bio-bots can be steered in different directions with light or chemical gradients. 3-D printing has become a major boon for these engineers as creating different shapes and designs has become quick and easy.
We will keep you updated on this research. Till then, let us know what are your thoughts on bio-bots through comments.
Source: #-Link-Snipped-#
Replies
You are reading an archived discussion.
Related Posts
A team from University of Washington researchers, led by Maya Cakmak and Rajesh P. N. Rao, has developed a new way of Goal-based Imitation Learning. The computer scientists have shown...
Barring a few exceptions, Samsung has been notorious for selling devices that offer sub-par performance in the high-end tablet market. But this time, Samsung has really outdone its previous releases...
IRCTC has launched a new railway ticket booking site: https://nget.irctc.co.in and it looks like the new site is quite faster even during the peak traffic hours. Ticket booking seems to...
Videocon has announced VPhone Grande, a budget phone priced at Rs. 1950.00 for Indian mobile consumers. Budget phones we've seen so far (and we're talking about those priced under Rs....
Hii all,
I have tried to gather some viva questions(basics), please let me know if they are helpful. I am trying to collect few more.
