Binuclear Copper Complex Converts Carbon Dioxide To Organic Compound- Oxalate
The rapid increase in the level of pollutants like carbon dioxide (CO2) in the environment is a growing concern and many researches are going on in this field in order to reduce its atmospheric presence. One such research was carried out by the researchers of Louisiana State University (LSU) and their work was published in the Journal Nature Communications on December,19. The research team has discovered a binuclear copper complex that converts carbon dioxide to oxalate (C2O42−) by applying a three-step reaction sequence. In other words, this new method converts CO2 into a useful organic compound.
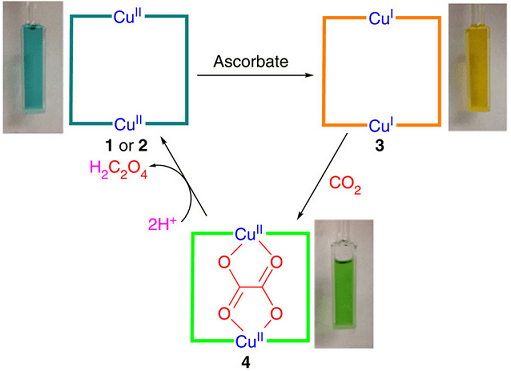
Diagrammatic representation of conversion of CO2 to oxalate
The team led by Andrew Maverick, Professor of Chemistry and acting associate dean in the LSU College of Science, performed three-step reaction sequence with help of a mild reducing agent. The process starts with the reduction of cyclic copper (II) complex to copper (I) in a solution. The reduction is done electrochemically or using sodium ascorbate (vitamin C). After that, the CO2 present in the air is fixed into oxalate as the reduced complex selectively reacts with it. Then, the bridging of oxalate ion between two copper atoms takes place, which leads to its release as oxalic acid after treating with mineral acids. This leads to the regeneration of original copper complex as oxalate and the completion of the process.
Developing a compound that would react with CO2 was a herculean task as CO2 does not react with any compound easily. The team formed more than 50 distinct compounds before creating copper complex. According to Maverick, even highly energetic molecules many times do not react with CO2 and to find a compound that can convert CO2 into something with a little more stored energy was of great significance while performing the research.
The major drawback of this research is that the compound takes four to five days to react. Therefore, the team is currently focusing on this factor. They are also trying to find other compounds and catalysts that will speed the conversion process.
Source: #-Link-Snipped-#| #-Link-Snipped-#
Diagrammatic representation of conversion of CO2 to oxalate
The team led by Andrew Maverick, Professor of Chemistry and acting associate dean in the LSU College of Science, performed three-step reaction sequence with help of a mild reducing agent. The process starts with the reduction of cyclic copper (II) complex to copper (I) in a solution. The reduction is done electrochemically or using sodium ascorbate (vitamin C). After that, the CO2 present in the air is fixed into oxalate as the reduced complex selectively reacts with it. Then, the bridging of oxalate ion between two copper atoms takes place, which leads to its release as oxalic acid after treating with mineral acids. This leads to the regeneration of original copper complex as oxalate and the completion of the process.
Developing a compound that would react with CO2 was a herculean task as CO2 does not react with any compound easily. The team formed more than 50 distinct compounds before creating copper complex. According to Maverick, even highly energetic molecules many times do not react with CO2 and to find a compound that can convert CO2 into something with a little more stored energy was of great significance while performing the research.
The major drawback of this research is that the compound takes four to five days to react. Therefore, the team is currently focusing on this factor. They are also trying to find other compounds and catalysts that will speed the conversion process.
Source: #-Link-Snipped-#| #-Link-Snipped-#
Replies
-
 Joseph ChristieI am a bit confused about"the binuclear copper complex that converts carbon dioxide to oxalate (C2O42−) by applying a three-step reaction sequence." No information is provided regarding the structure of"the cyclic copper (II) complex to copper (I) in solution." Presumably the reaction path is radical in nature by a SET or single electron transfer. Moreover, Cu (I) complexes are insoluble in aqueous media and complexing agents are usually organic amines .
Joseph ChristieI am a bit confused about"the binuclear copper complex that converts carbon dioxide to oxalate (C2O42−) by applying a three-step reaction sequence." No information is provided regarding the structure of"the cyclic copper (II) complex to copper (I) in solution." Presumably the reaction path is radical in nature by a SET or single electron transfer. Moreover, Cu (I) complexes are insoluble in aqueous media and complexing agents are usually organic amines .
Statement, "Developing a compound that would react with CO2 was a herculean task as CO2 does not react with any compound easily" is not correct since RLi or butyl lithium reacts with CO2 to form the carboxylate in a facile reaction.
You are reading an archived discussion.
Related Posts
Any idea how is it to take up Master of Science- Technology in Computer Science (distance education) from Manipal University ?Is it equivalent to MS or M.tech or its a...
The autonomous car which Google revealed in this year's May has completed its closed-door tests and may now hit the public roads in the first month of the coming year....
Earlier this month, the Indian mobile manufacturer Lava launched Iris Fuel 60 with a whooping 4000mAh battery and now the company has launched a new entry-level smartphone Iris 310 Style....
The much awaited Microsoft Windows 10 OS will probably feature a brand new browser which is not the Internet Explorer. The new browser, codenamed 'Spartan' looks and feels as more...
BugClipper is a privately held Computer Software company founded by Puneet Sharma and Narendra Kumar in the year 2013. BugClipper specializes in Mobile Testing, Bug Tracking, iOS, Android and Web...
